
- Home
- Solutions
- Business Optimization
- Fastening Design Center
- Nail Selection Guide
QUICK GUIDE TO SELECTING THE RIGHT NAIL FOR CONCRETE
Direct fastening on concrete
Not all nails are created equal
There’s a large variety of nails to choose from for direct fastening applications. It’s not always easy to understand the differences between the various nail types and to select the right nail for your needs.
Our fastening systems are designed to achieve maximum performance in a wide range of applications.
What determines nail performance
Multiple factors such as concrete properties, nail design and the fastening system used can influence how a nail performs on your jobsite.
The three main factors that define the suitability of a nail for use on concrete are: stick rate (i.e. the percentage of nails that hold securely), holding values and the cost of the nail.
How should you select the right nail for concrete?
Read on and find out more about the influencing factors.
1. Concrete basics
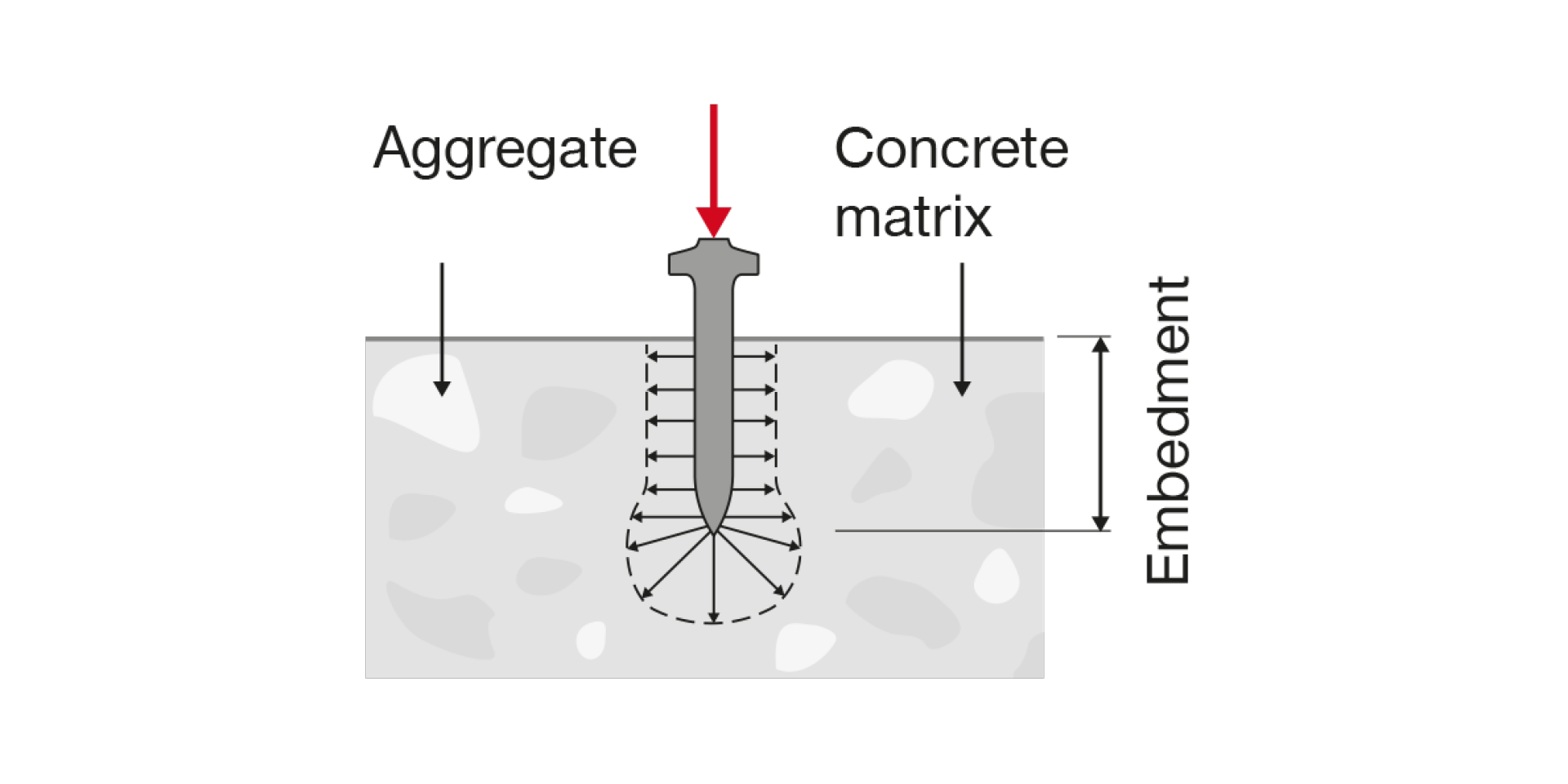
A nail penetrating concrete needs to create a hole for the shank by crushing and compacting the concrete. It also needs to withstand hitting hard aggregates as it finds its way into the concrete matrix. The resulting holding value achieved by the nail is directly linked to its embedment depth.
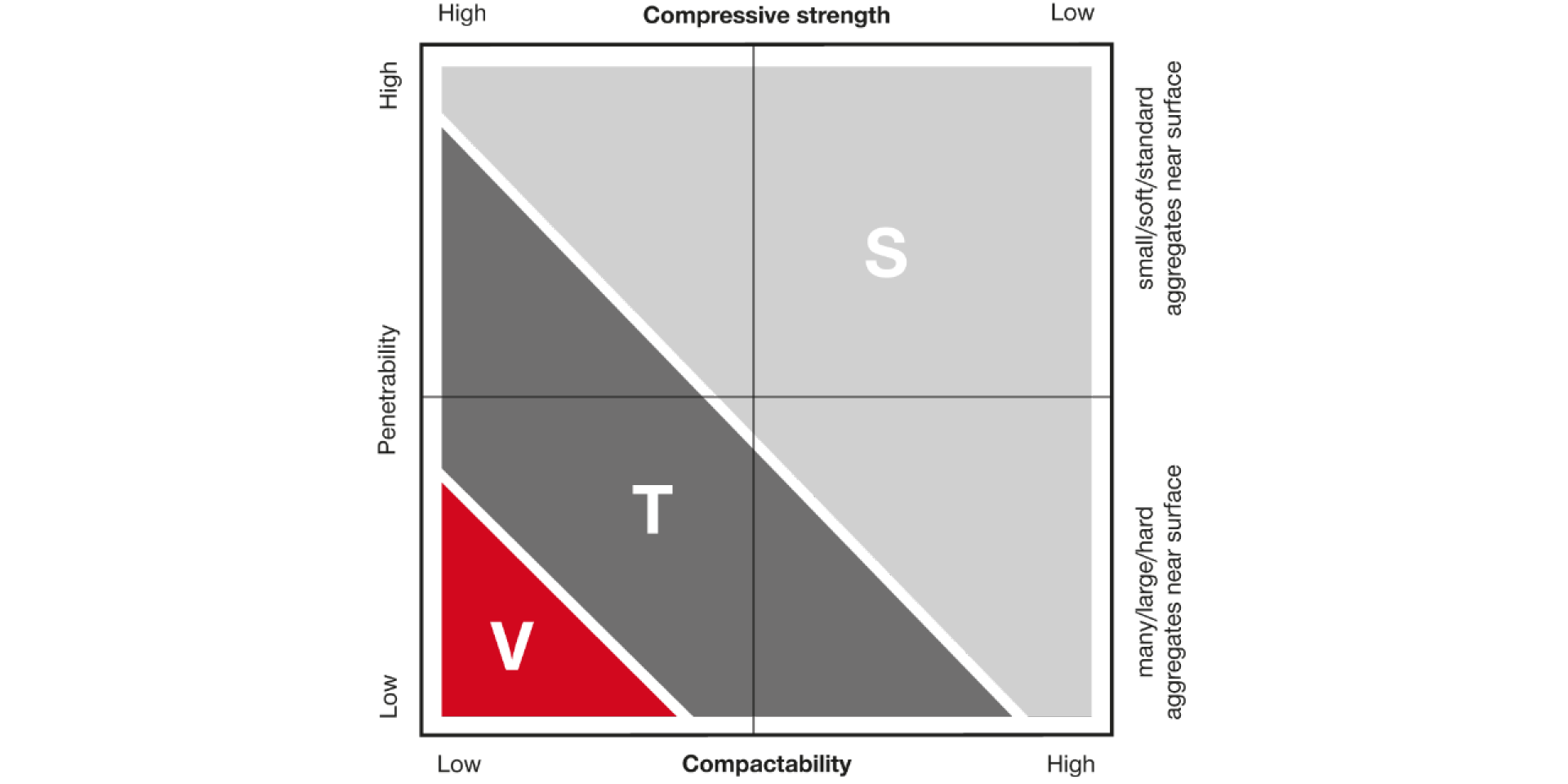
We distinguish between three concrete types:
Soft (S)
- Low compressive strength (e.g. 2-5 ksi)
- Small to medium-size aggregates; e.g. soft limestone
- Example: lightweight concrete
Tough (T)
- Medium to high compressive strength (e.g. 5-7 ksi)
- Medium-size aggregate; e.g. pit gravel
- Example: normal-weight concrete
Very tough (V)
- High compressive strength (e.g. ≤ 7 ksi)
- High proportion of large aggregates, mainly hard; e.g. quartz, granite
- Example: high-performance concrete, very old concrete
2. Nail features
Penetrability and compactability, i.e. a nail's ability to penetrate and compact the concrete, are strongly influenced by three nail design features:
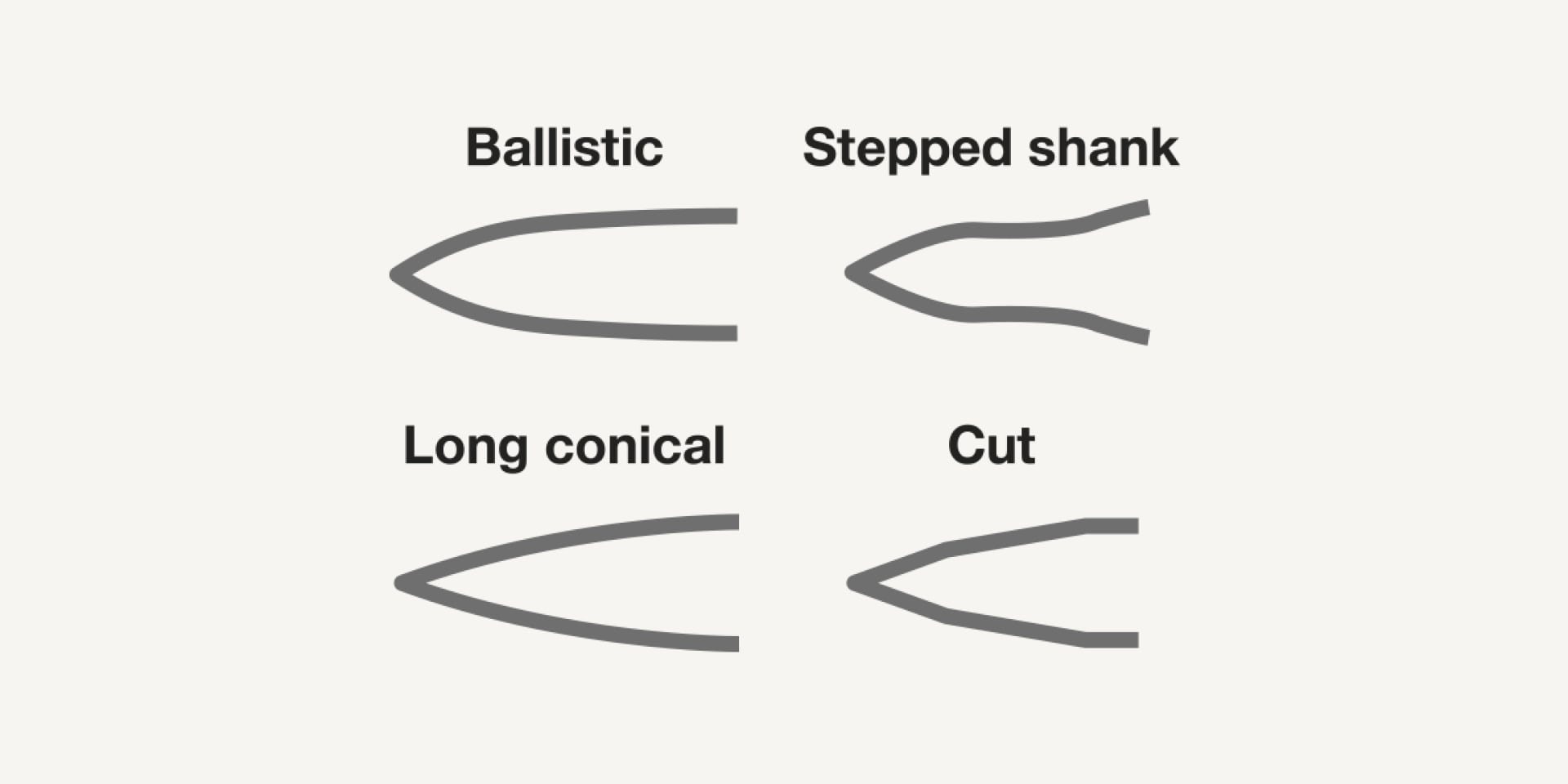
The shape of the tip influences how well a nail is able to penetrate the concrete. Four different shapes are in use. The cut tip, the ballistic tip, the stepped shank and the long conical tip.
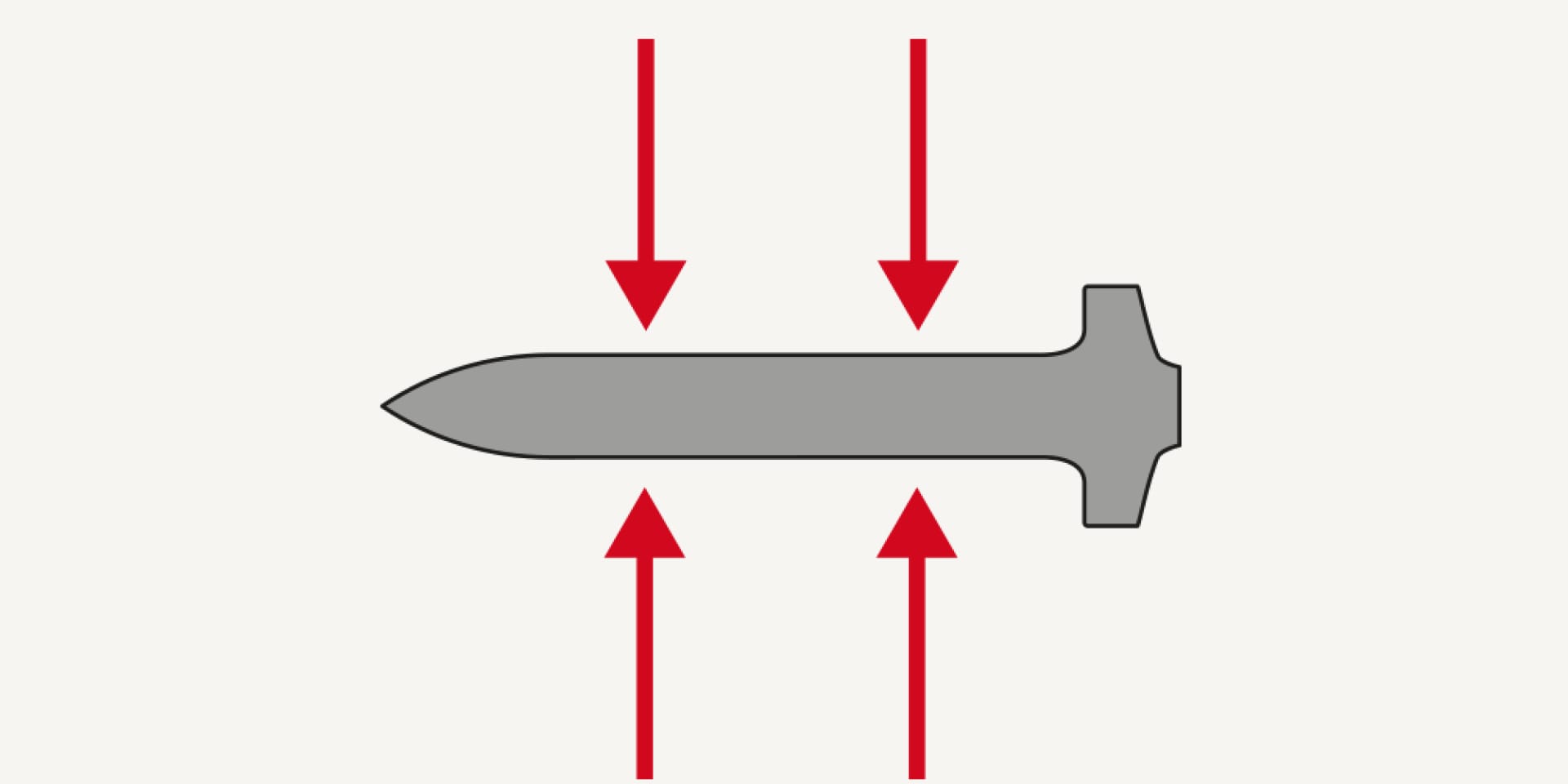
Length and diameter also affect how easily the nail penetrates the concrete.
A nail’s hardness influences how likely it is to be driven successfully. A harder nail is easier to drive into hard material. However, if the nail is too hard, it will break instead of bending when it hits a hard aggregate in the concrete. Therefore, a good nail is hard with enough ductility to bend, not break when hitting an aggregate.
3. Factors influencing your nail choice
The three factors that matter most in direct fastening applications are:
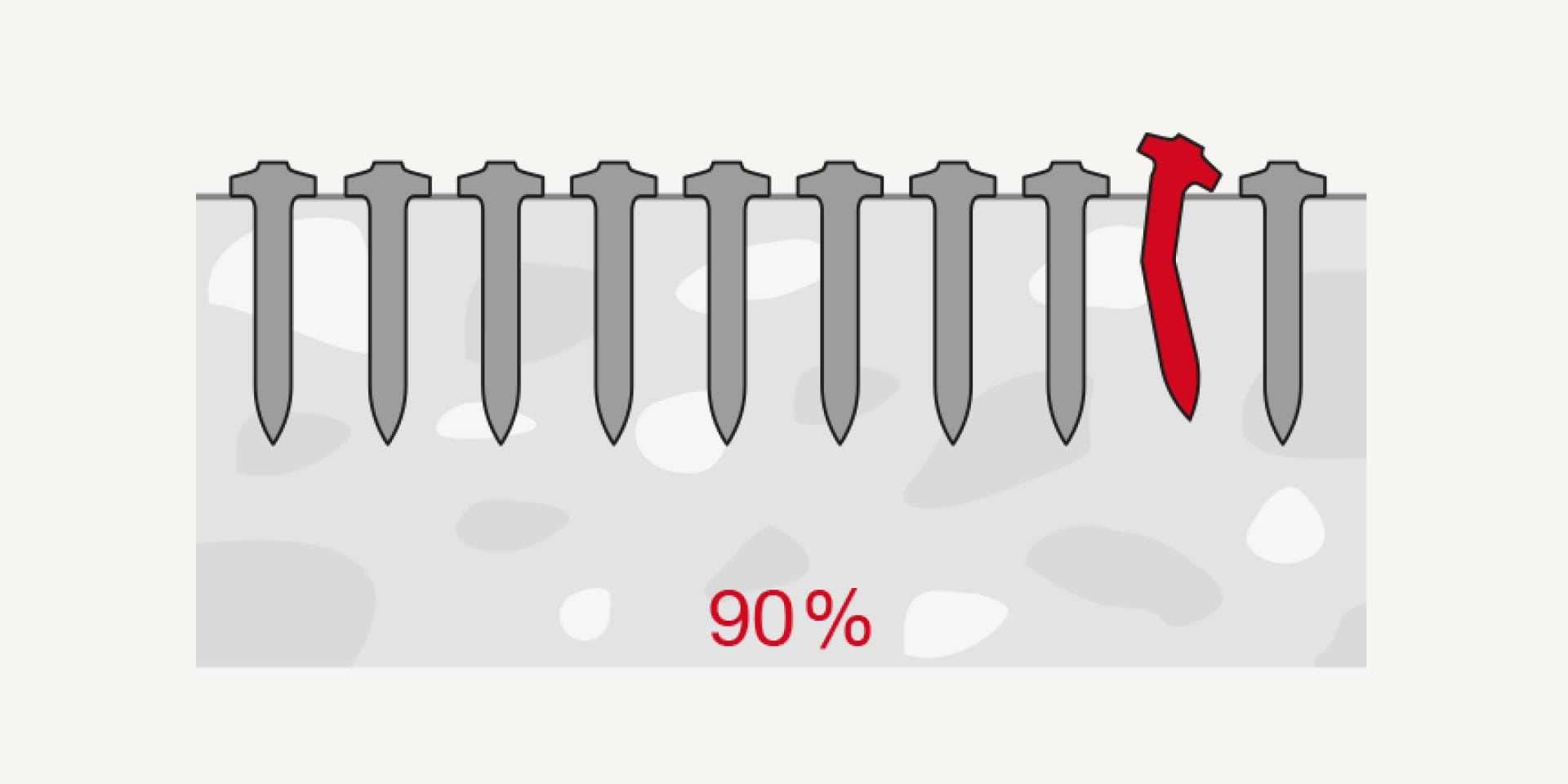

The stick rate indicates the percentage of nails being properly driven to the correct depth, i.e. with the permissible nail stand-off.
Holding values provide a measure of a nail's load-bearing capability. Loads can be split into two types: shear and tension. Shear loads act at right angles to the shank of the nail and tensile loads are concentric.
The wide range of Hilti nails offers the most cost-efficient solution for various applications by allowing you to choose exactly the right nail for your requirements.
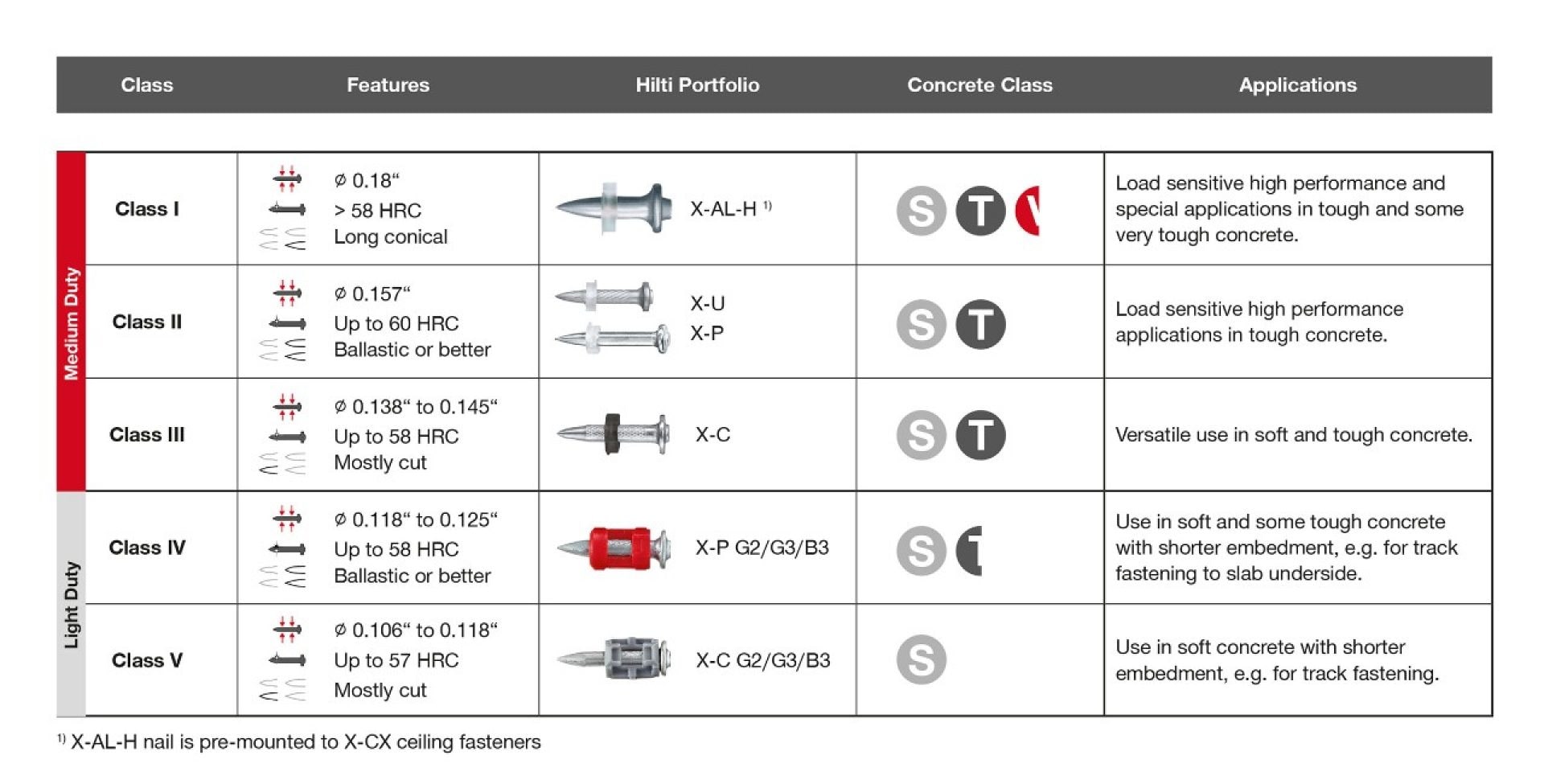
4. Nail classes
Different nails have been developed for various applications. They can be grouped in the five classes illustrated in the table below.
In general, assuming the nail is suitable for your application, light duty class V nails present the most economical solution as they are the least costly. Cost is directly related to the manufacturing technologies involved as well as the material from which the nails are made. Each higher nail class performs better under harsher conditions than the one below, but the manufacturing costs, and thus the price of the nail, increase with each nail class.
5. Embedment
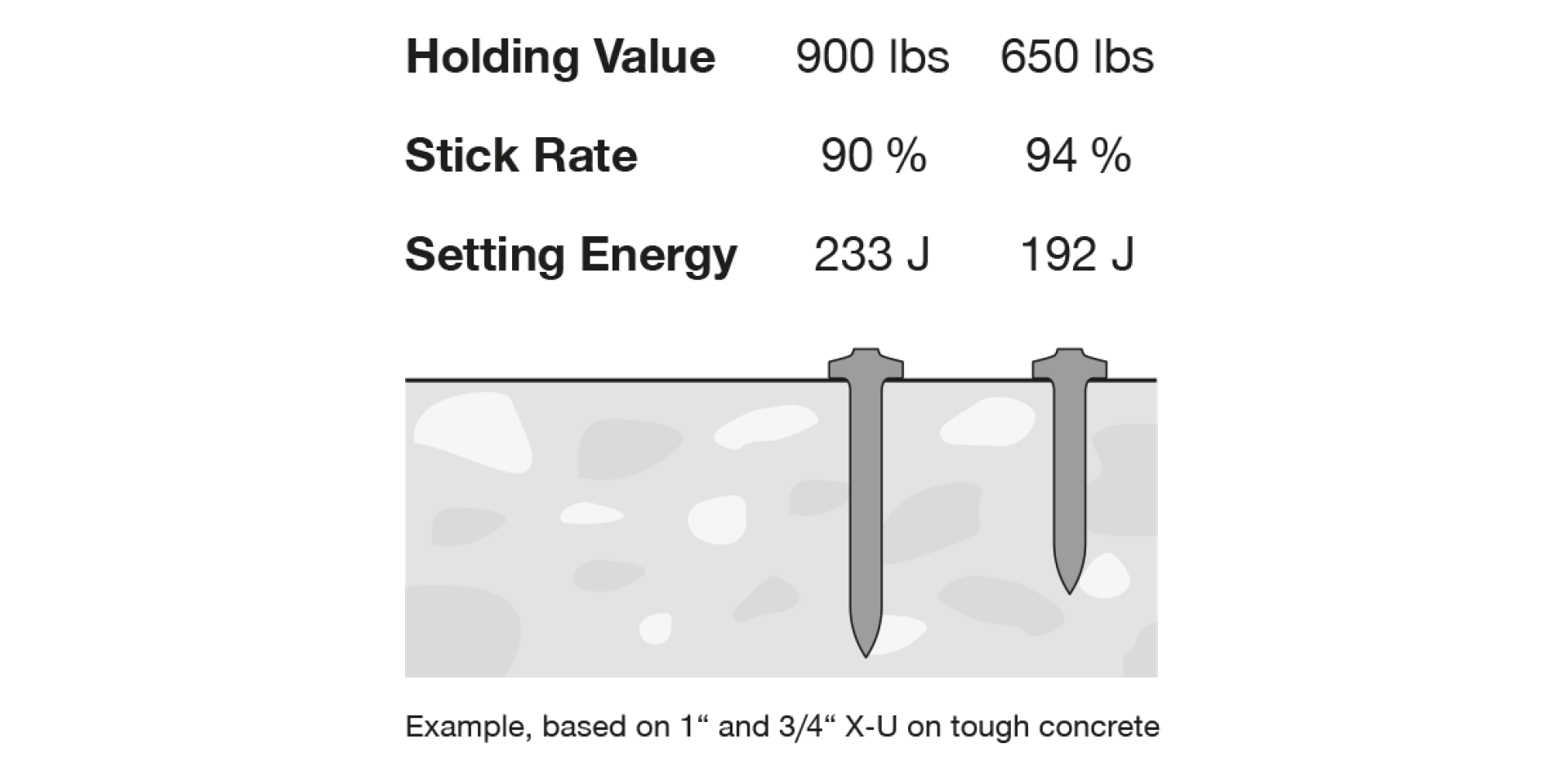
An additional factor that influences nail performance is depth of embedment.
A nail that can be driven deeper generally has the ability to hold higher loads. However, if a nail needs to be driven deeper, there are two side effects: The stick rate decreases and higher driving energy is required because the nail has to penetrate further into the concrete.
6. Nails and concrete
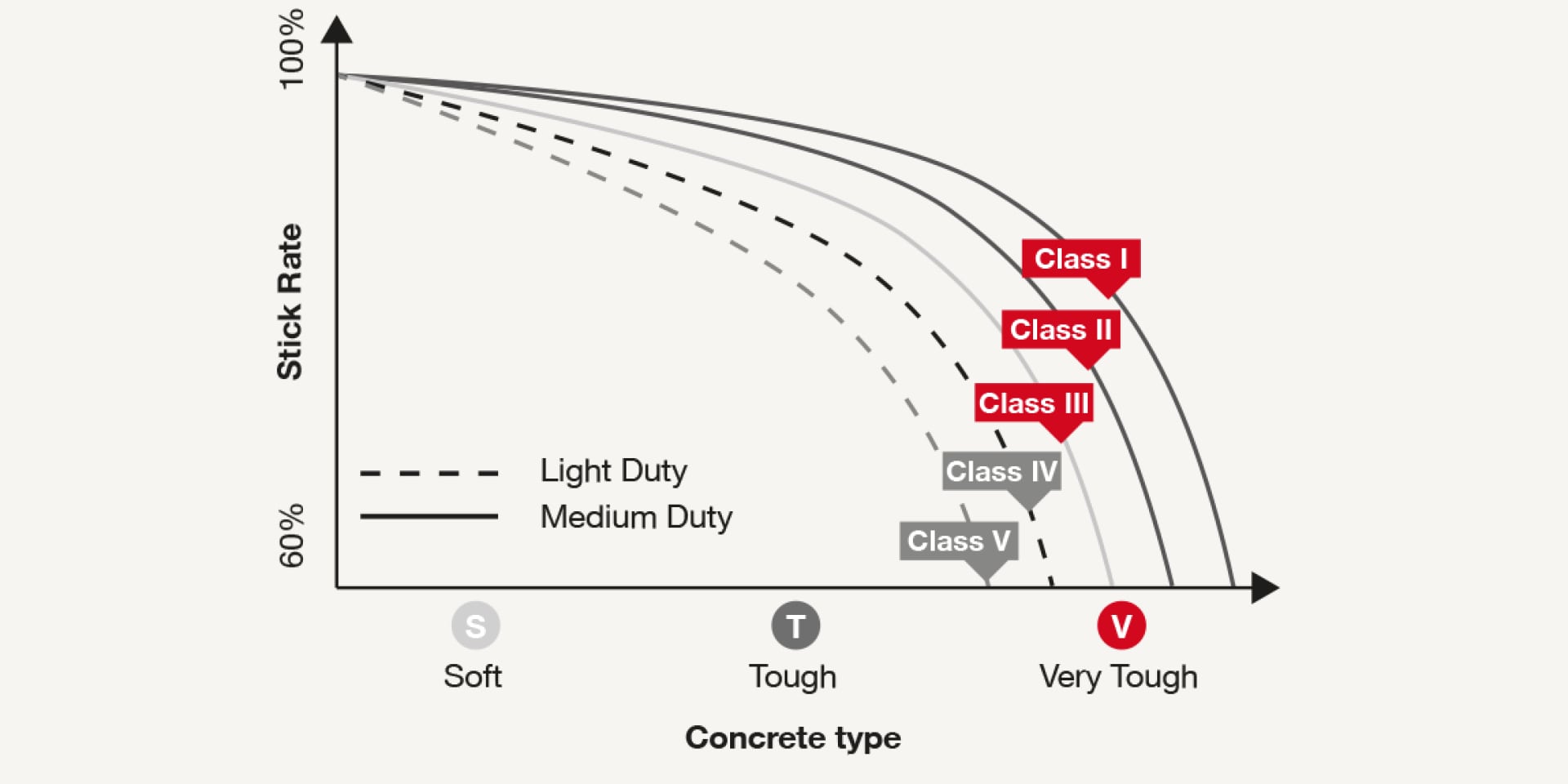
Nail performance varies depending on the type of concrete and the distribution of its aggregates. Nails of all classes perform similarly in soft concrete, but as the concrete gets tougher, the stick rate varies.
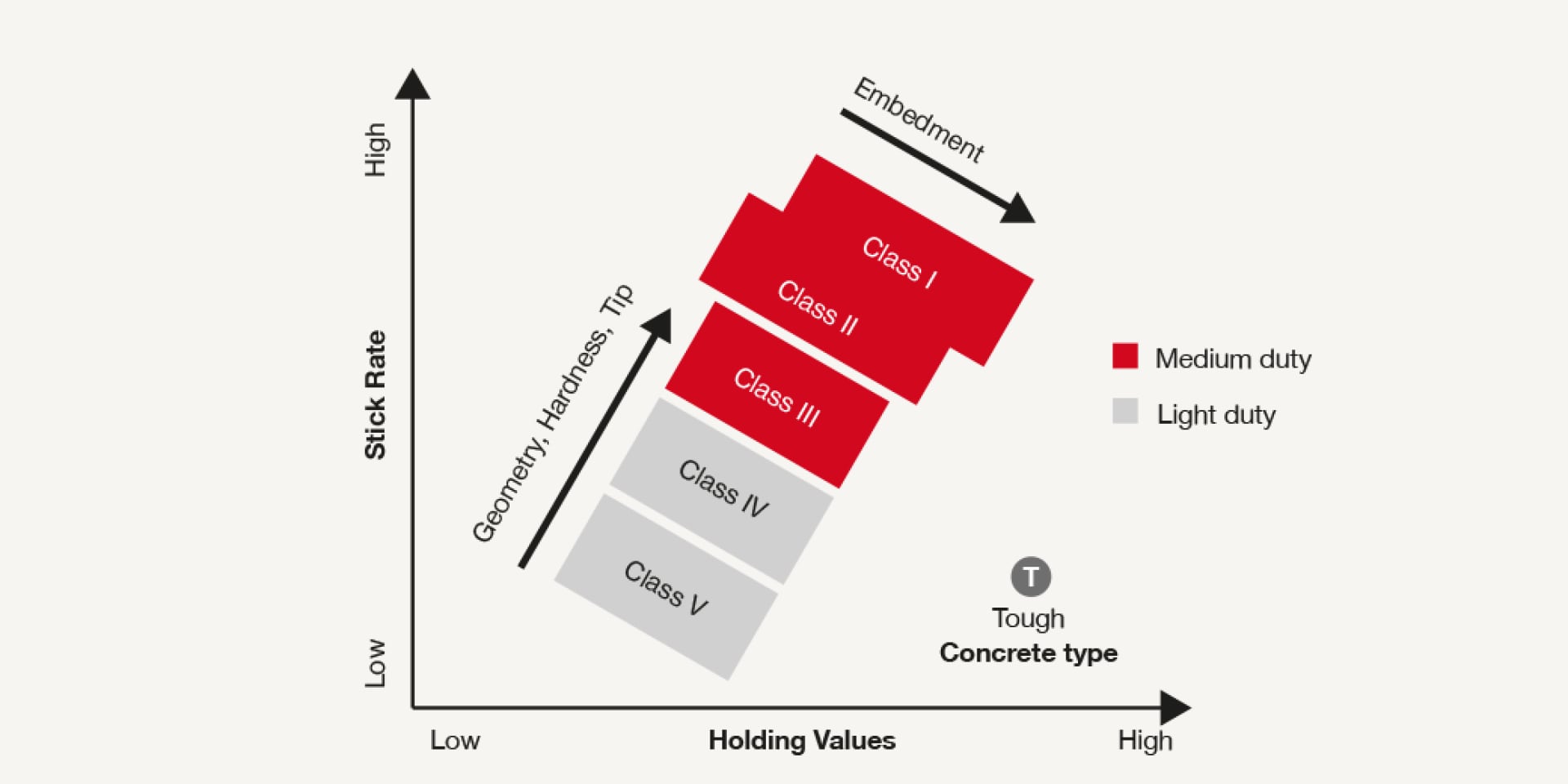
Differences between nails become clear in tough concrete. Premium nails perform better than less costly counterparts. See how depth of embedment, nail geometry, hardness and tip shape vary between nail classes.
7. Hilti systems
Our fastening system help to ensure that nails are correctly driven by achieving maximum nail perpendicularity, good nail guidance and thorough use of the appropriate driving energy.
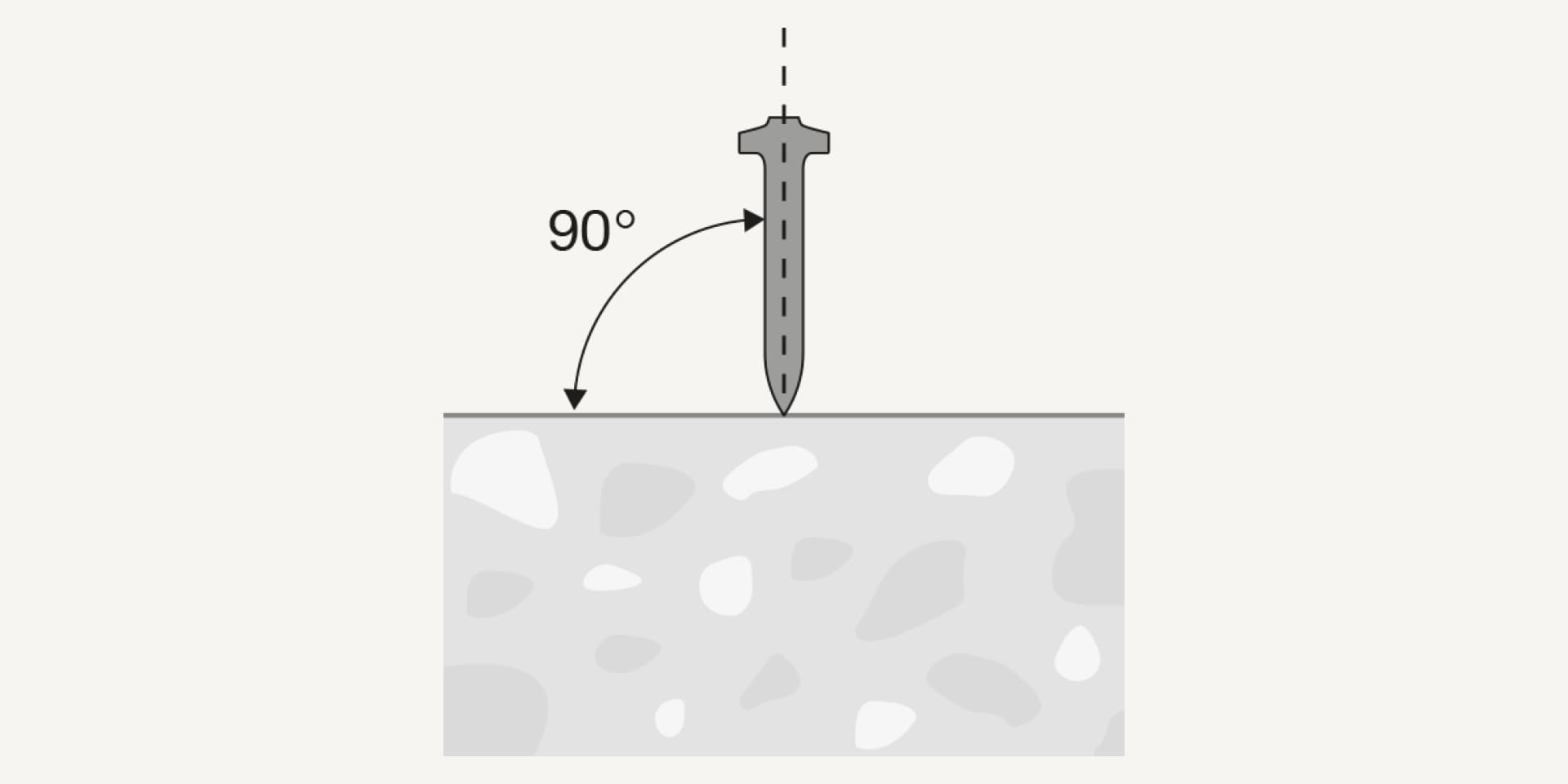
Our fastening tools help to keep nails perpendicular to the working surface, thus eliminating failures caused by attempting to drive the nail at an angle.
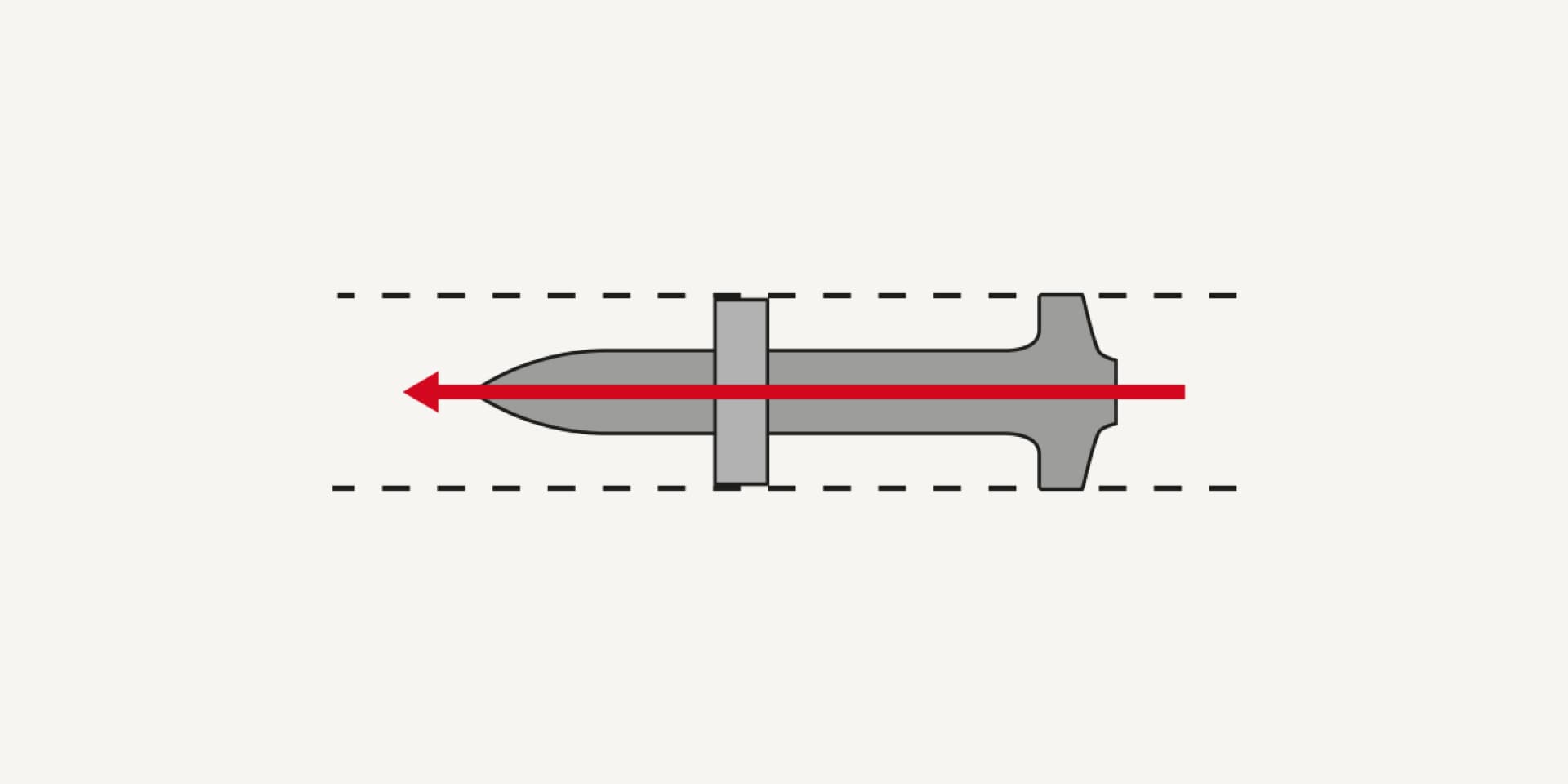
Thanks to excellent nail guidance in the tool and the use of solid washers, the nail leaves the tool at the angle you intend.
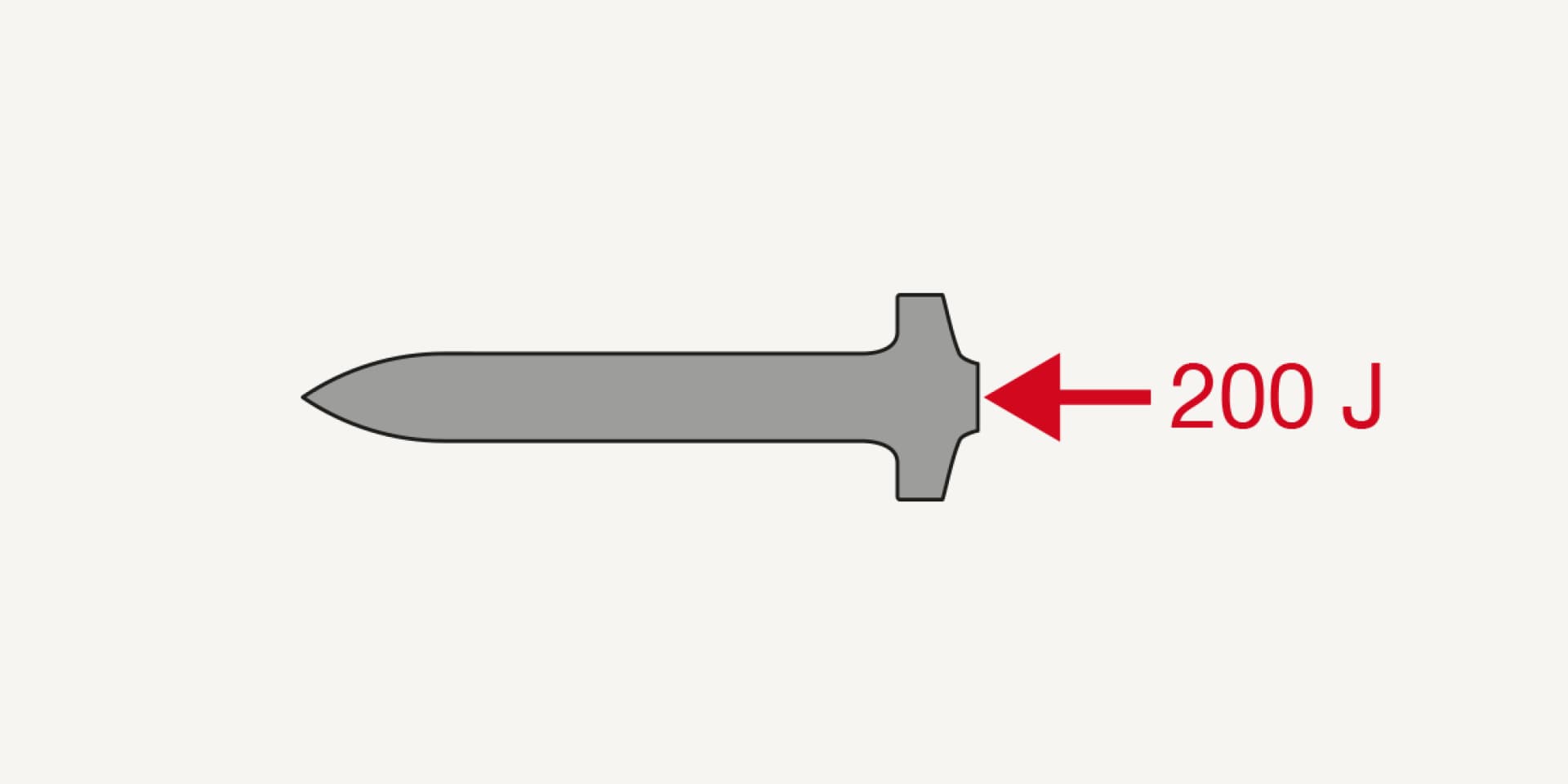
The nail driving energy released by a Hilti tool is precisely controlled to ensure reliable achievement of the desired embedment depth.
8. Selecting the right nail for your requirements
Here are four simple steps to help guide you to the right nail:
- Understand the application
- Be specific about what requirements are important
- Get to know the Hilti range of nails
- Then choose the right nail on the basis of your requirements
Following these four steps will help you:
- Maximize the stick rate
- Achieve the required holding values
- Select the most cost-efficient nail
- Achieve optimum embedment depth based on selecting the appropriate cartridge and adjusting the power setting
9. Recommended products
Make your selection
-
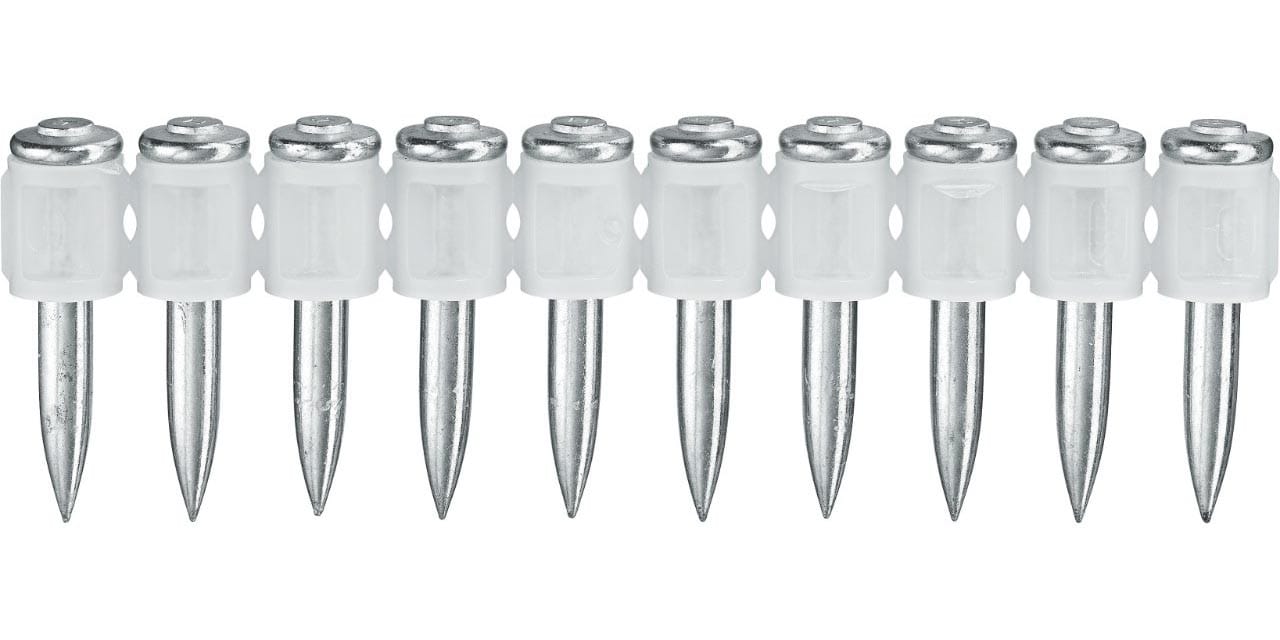

X-P MX
More information
X-P B3 MX
More information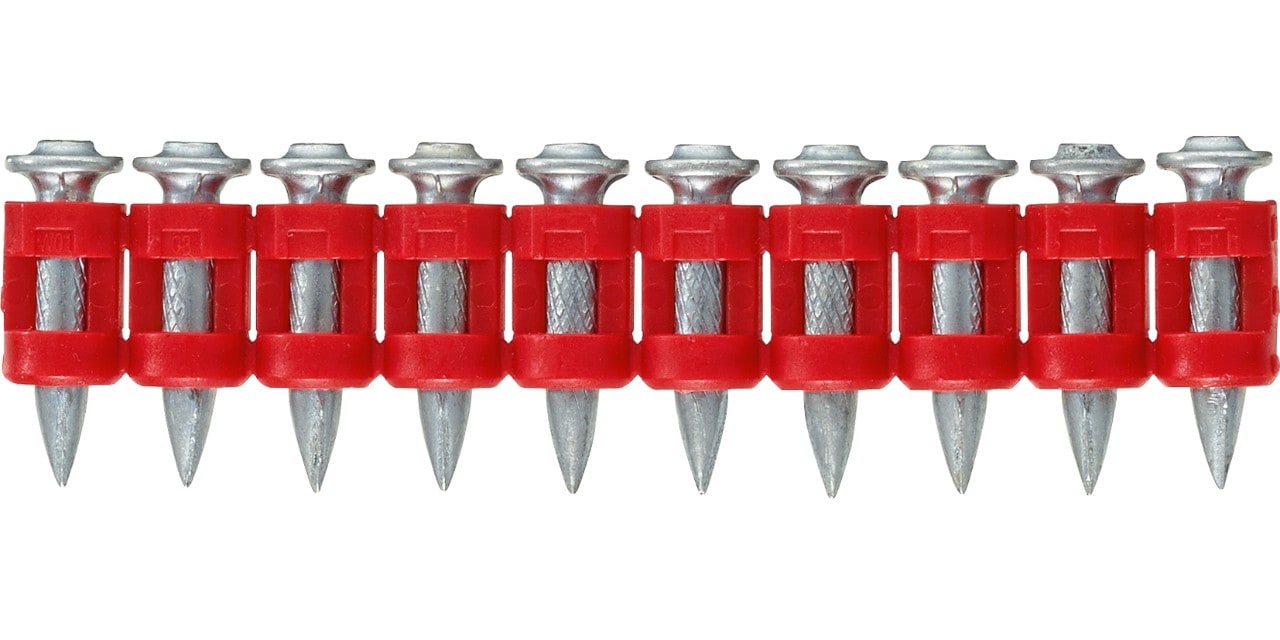
X-P G2 MX
More information
10. Want to know more?
For more information regarding our nails and their specifications, please refer to the Hilti Technical Guide Or, download our nail selector app, which is available in select countries.
Product Technical Guide Volume 1 - Direct Fastening
